Revolutionizing Finance: How Distributed Ledger Technology Transforms Transactions, Security, and Efficiency
What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
Distributed Ledger Technology is built on several core principles that differentiate it from traditional centralized ledger systems. At its heart lies decentralization, where data is distributed across a network of nodes rather than being controlled by a single central authority. This decentralization is facilitated through peer-to-peer networks, where each node in the network has a copy of the ledger.
The process works by replicating data across all nodes in the network. When a new transaction occurs, it is broadcast to the network and verified by nodes using consensus algorithms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Once verified, the transaction is added to a block, which is then linked to previous blocks through cryptographic hashes, forming a chain of blocks – hence the term blockchain.
DLT can be categorized into different types: public, private, permissioned, and permissionless ledgers. Public ledgers are open to anyone and are typically used in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Private ledgers are restricted to specific organizations and are often used within companies. Permissioned ledgers allow only authorized parties to participate, while permissionless ledgers are open but may have certain restrictions on who can validate transactions.
Transformation in Financial Transactions
One of the most significant impacts of DLT is its ability to enhance transaction efficiency. Traditional cross-border payments can take days and involve multiple intermediaries, leading to high costs and inefficiencies. With DLT, these transactions can be completed in minutes or even seconds without the need for intermediaries like banks.
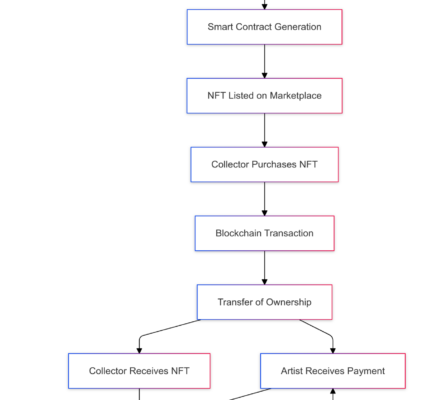
Smart contracts play a crucial role in trade finance by automating processes that were previously manual. These self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into lines of code can reduce inefficiencies significantly. For instance, in supply chain finance, smart contracts can automate payment releases based on shipment confirmations, reducing the risk of fraud and speeding up the payment process.
In banking and finance, DLT is being used for various applications such as Know Your Customer (KYC) processes and digital identity solutions. These applications streamline customer onboarding, reduce compliance costs, and enhance security by ensuring that customer data is accurate and tamper-proof.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
The security benefits of DLT are substantial. By using cryptographic algorithms, DLT ensures that data is encrypted and protected from unauthorized access. The decentralized nature of DLT makes it resilient to attacks and system-wide failures; if one node goes down, others can continue to operate without interruption.
Transparency is another key advantage of DLT. All transactions are recorded on a public ledger that can be viewed by anyone with access to the network. This transparency reduces the risk of fraud and manipulation because all transactions are time-stamped and immutable once added to the blockchain. In contrast to traditional centralized systems, where data can be altered or deleted, DLT ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered without consensus from the entire network.
Efficiency and Cost Reduction
DLT significantly reduces transaction costs by eliminating the need for intermediaries and central authorities. In traditional systems, intermediaries like banks charge fees for facilitating transactions. With DLT, these fees are minimized or eliminated altogether because transactions are direct and peer-to-peer.
In supply chain management, DLT provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, shipment status, and other critical data points. This real-time visibility reduces paperwork, minimizes inefficiencies, and ensures that all stakeholders have access to accurate information simultaneously. For example, companies like Maersk have implemented blockchain solutions to track shipments more efficiently and securely.
Industry Applications Beyond Finance
While DLT has made significant inroads in finance, its applications extend far beyond this sector. In government, DLT can be used for real estate title transfers, ensuring that property ownership records are secure and tamper-proof. In healthcare, patient records can be stored securely on a blockchain, ensuring confidentiality while allowing authorized access.
Other sectors where DLT is making an impact include aviation (e.g., tracking aircraft maintenance records), education (e.g., verifying academic credentials), and manufacturing (e.g., tracking product authenticity). These diverse applications highlight the versatility of DLT in solving complex data management problems across various industries.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its transformative potential, DLT faces several challenges. One major issue is scalability; current blockchain technologies struggle to handle high transaction volumes efficiently. Additionally, substantial computing resources are required to maintain these networks, which can be energy-intensive.
However, as technology evolves, these challenges are being addressed. New consensus algorithms like Proof of Stake (PoS) are more energy-efficient than traditional Proof of Work (PoW). Moreover, innovations like sharding and off-chain transactions are improving scalability.
Looking ahead, DLT is poised to have a transformative impact on corporate treasury management, digital assets trading, and global financial systems. As more organizations adopt this technology, we can expect to see streamlined processes, enhanced security measures, and increased efficiency across the board.